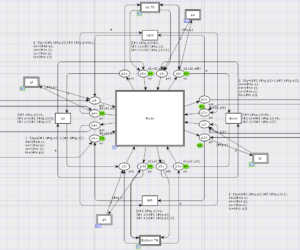
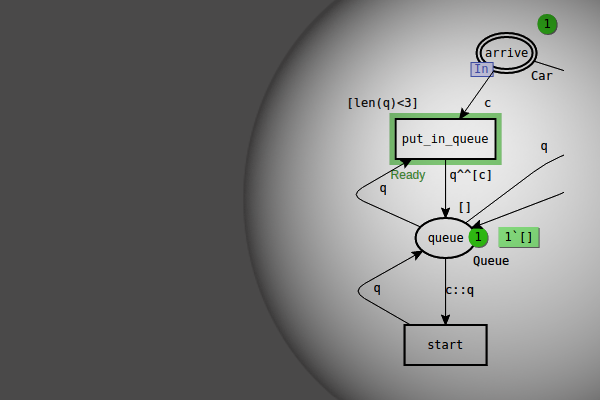
The model has the same structure for any given PBB network. It evaluates the maximal and average network response time on-fly. The network topology is inputted as a value of dedicated constant together with other parameters such as addresses of various types of terminal and communication equipment their performance and the number of ports. Reenterable models are devised for model-driven design of networks. Dmitry A. […]
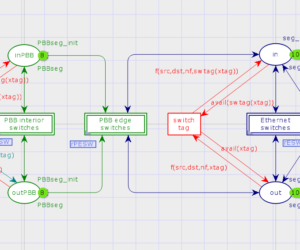
Reenterable Model of Rectangular Communication Grid with Cut-through Nodes
A reenterable model of communication grid with cut-through nodes is constructed. The cut-through transmission of packets works fast, because it uses only the head of packet, which contains the destination address, for the forwarding decision. The reenterable models of the grid structures do not depend on the grid size that is the main advantage of reenterable models. The grid performance and average packet delivery time […]
Reenterable Model of Rectangular Communication Grid
A reenterable model of communication grid with store-and-forward (SAF) nodes is constructed. The reenterable models of the grid structures do not depend on the grid size that is the main advantage of reenterable models. The grid performance and average packet delivery time are evaluated for various intensity of Poisson and Uniform distributions. Shmeleva T.R. Efficiency estimation of computing grids with various traffic types. Proceedings […]
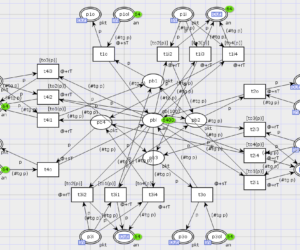
Rectangular Grid with Cut-through Switching Nodes
The model is composed of packet switching nodes situated on a rectangular grid and generators of traffic attached to the grid borders. It is supplied with malefactor models in the form of traffic guns disguised under regular multimedia traffic. Switching nodes use cut-through transmission of packets that works fast, because it uses only the head of packet, which contains the destination address, for the forwarding […]
Rectangular grid under disguised traffic attack
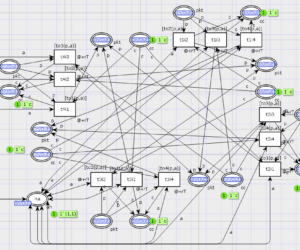
The model consists of an 8×8 matrix of switching nodes that deliver packets to computing nodes which are attached to the matrix borders and produce and consume packets. Traffic guns are added to the model to represent traffic attacks. Simulation in CPN Tools revealed simple and dangerous traffic gun configurations. D. A. Zaitsev , T. R. Shmeleva, W. Retschitzegger, B. Pröll Security of grid structures […]
Source Code
GUI No documentation currently available. Simulator If you are on Windows, you need a recent version of Cygwin You need a patched version of SML/NJ to get started. In some directory run bin/buildml where is the minor version you wish to install, e.g., 73. The directory created before must be added to your path Test that SML/NJ installed correctly by executing sml Then try executing […]
Random distribution functions
Term definitions Random-number generator: A function that generates numbers that are uniformly distributed over the interval (0,1). Random-variate generator: A function that generates numbers whose probability distribution is different from that of the uniform on the interval (0,1). Random-variate generators Below is a brief summary of the random-number generators that are available. Click on a function name to see a more detailed explanation. bernoulli(p:real) : […]
Bernoulli
Function for generating values from Bernoulli distributions. Interface bernoulli(p:real) : int where 0.0<=p<=1.0. The value returned is either 0 or 1. The function returns a drawing from a Bernoulli distribution with probability p for success (i.e., success=1). It raises Bernoulli exception if p<0.0 or p>1.0. Characteristics Mean: p Variance: p(1-p) Example bernoulli(1.0/6.0) Throw a die and observe if a six was thrown. This experiment has […]
Beta
Note: Introduced in CPN Tools 3.2.2. Interface beta(a:real, a:real) : real where a,b>=0.0. Returns a drawing from a beta distribution with parameters a and b. Raises Beta exception, ifa<=0.0 or b<=0.0. Related pages Random distribution functions
Binomial
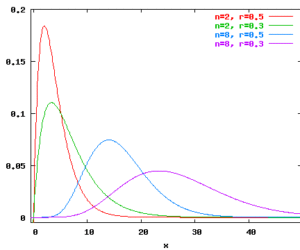
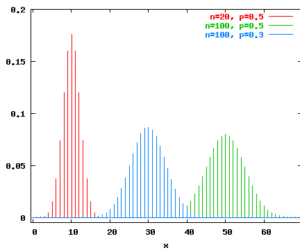
Function for generating values from binomial distributions. Interface binomial(n:int, p:real) : int where n>=1 and 0.0<=p<=1.0. This function returns a drawing from a binomial distribution with n experiments and probability p for success. It raises Binomial exception if n<1 or p<0.0 or p>1.0. Characteristics Mean: np Variance: np(1-p) Probability mass functions for binomial distributions: Example binomial (100, 1.0/6.0) Throw a die 100 times and observe […]